Top view Side view
This disk scanner needs some
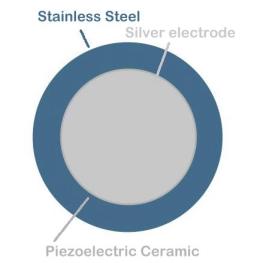
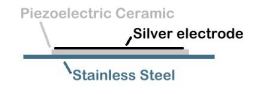
explanation. It uses a modified Unimorph disk. Unimorph disks are
one of the most common piezoelectric devices available. They are most often
used for small sound generators, speakers, buzzers. A Unimorph disk is
made of two disks bonded together, one is a piezoelectric ceramic the other
is metal. The metal disk makes it much less fragile than the ceramic
alone.


Top view
Side view
The piezo ceramic expands
or contacts when an electric field is applied to the disk. A standard
Unimorph disk bows up or down as a voltage is applied between the metal
disk and the silver electrode. The Unimorph disk used in this design moves
about 0.16 mm/Volt,
and its natural resonance frequency is approximately 2.5 kHz.
 Bow Up
Bow Up
 Flat
Flat
 Bow down
Bow down
I modified the standard Unimorph
disk to get scanner motion in all three axis. My design divides the electrode
into four quadrants, and I add a standoff at the center.
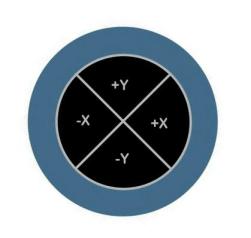
As the voltage on opposing
electrodes are changed the angle at the center of the disk is changed.
Because the voltage causes a change in angle the motion in the X-Y plain
is directly proportional to the length of the standoff.
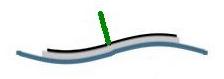
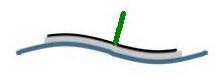 Scanner X,Y motion
Scanner X,Y motion
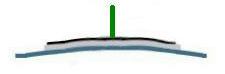
 Scanner Z motion
Scanner Z motion
References
Patent
US5866902:
Atomic force microscope with integrated optics
for attachment to optical microscope
Inventors: John Alexander, Marco Tortonese, and Thai Nguyen
Home Simple STM Project Home Project Overview Progress
Mechanical Design
Disk Scanner Description How to Make a Disk Scanner Mechanical Approach
Mechanism
Mechanical Bill of Materials Electronics Design Electronics Schematics
Electronics Bill of Materials Operating the STM Images